200K Layoffs, $100B Lost: The Tsunami of China’s Regulation on Education
Analyzing the impact of China’s regulatory crackdown on the nation’s for-profit education industry.
After a series of fines and restrictions on for-profit online tutoring companies, the China’s Ministry of Education released a final document titled “Opinions on further reducing the workload of students in compulsory education and the burden of off-campus training” on July 24, 2021, which is also called “The Double Reduction Policy”.
The policy aims to reduce learning pressure on both students and parents, as well as encourage couples to have children to counter China’s declining birth rate and the “involution effect” plaguing the nation.
But the policy, which imposes a series of harsh regulations, has had an immediate and unprecedented impact on for-profit tutoring companies and their employees, effectively marking the end of an era for the for-profit tutoring industry in China.
In this exclusive Class Central analysis, we summarize the immense impact this policy has had in China.
You can click on a section to skip to it:
- China education stocks plummet
- Education companies go bankrupt
- End of many curriculum-based tutoring businesses
- Layoffs of a large number of employees
- Suspending fundraising and withdrawing IPO application
$100 Billion Wiped Off China’s Education Market Cap
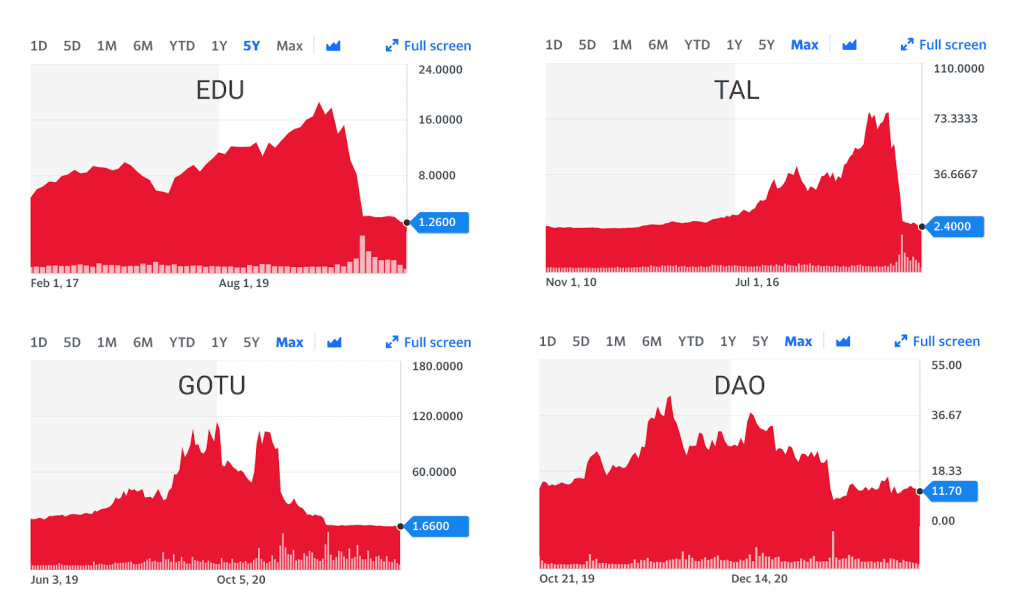
Since the release of the document “Key points of the Ministry of Education’s work” at the start of 2021, stock prices of US-listed education companies in China have seen a drastic drop and never bounced back.
The stock prices of US- and Hong Kong-listed companies reached a first low just after the “Double Reduction Policy” was introduced in July, 2021. As the new regulations started being enforced, stock prices went further down by over 90%.
More than $100 billion dollars were wiped off China’s education market cap.
| Company | Price
(Feb 15, 2021) |
Price
(Jul 26, 2021) |
Price
(Feb 15, 2022) |
Drop rate* |
| New Oriental Education & Technology Group Inc. (EDU) | $19.28 | $2.17 | $1.64 | -91% |
| TAL Education Group (TAL) | $90.15 | $6.07 | $3.78 | -96% |
| GSX Techedu Inc. (GOTU) | $103.27 | $3.19 | $2.46 | -98% |
| Youdao, Inc. (DAO) | $32.5 | $8.82 | $13.98 | -57% |
| China Online Education Group (COE) | $24.35 | $2.87 | $1.80 | -93% |
* The drop rate is calculated from Feb 15, 2021 to Jan 24, 2022.
| Company | Market Cap
(Feb 16, 2021) |
Market Cap
(Jul 26, 2021) |
Market Cap
(Jan 24, 2022) |
Loss* |
| New Oriental Education & Technology Group Inc. (EDU) | $33.49B | $3.27B | $2.78B | -$30.71B |
| TAL Education Group (TAL) | $52.54B | $2.84B | $2.44B | -$50.10B |
| GSX Techedu Inc. (GOTU) | $27.67B | $0.64B | $0.63B | -$27.04B |
| Youdao, Inc. (DAO) | $4.25B | $1.06B | $1.76B | -$2.49B |
| China Online Education Group (COE) | $0.55B | $0.06B | $0.04B | -$0.51B |
| Total | $118.5B | $7.9B | $7.7B | -$110.9B |
* The market cap loss is calculated from Feb 15, 2021 to Jan 24, 2022.
Under the “Double Reduction Policy”, Chinese education companies will no longer be allowed to raise capital through stock markets to invest in for-profit education businesses. Acquisitions, mergers, and foreign investment are also forbidden. Furthermore, companies are forced to shutter their tutoring business, even when they’re the company’s major source of revenue, and register as nonprofits for compulsory education.
Large Education Companies Go Bankrupt

More than 25 online tutoring companies have gone belly up in 2021, according to the report from “edu.100ec.cn”. Among them are several major education companies.
Juren Education, which was one of the oldest and largest K12 education companies in China, announced it would no longer provide services in the coming semester on its official WeChat account on August 31, 2021.
Juren Education was based in the Beijing Haidian district, home of well-known education institutions in China, and for 27 years provided courses in mathematics, English, and exam preparation for students from kindergarten to secondary school. Since its establishment in 1994, over 5 million primary and middle school students have been taught through Juren Education’s network of 60 schools across China.
Juren Education was acquired by US-listed company OneSmart International Education Group Limited. The company received a notice from NYSE for failing to file its annual report for the fiscal year that ended in August 2021. Executives from Juren Education announced that due to the lack of investment from their parent company, Juren was unable to pay salaries to its employees. As a result, hundreds of employees entered labor arbitration.
Over 13,000 students were affected by Juren’s closure, as the company was failing to refund close to 30 million yuan ($4.64 million). The company had already transferred over 15,000 students to other organizations according to Beijing News.
On August 11, 2011, another big company, Wall Street English, announced that its Chinese business had gone bankrupt. Wall Street English is an international adult English-training company founded in 1972. It entered the Chinese market in 2000 and had built over 71 learning centers in 11 cities across China, and had over 3000 employees at its peak.
The company targeted the high-end adult English training market with high course fees. The entry-level program cost 20–90K yuan ($3–14K) per year, and the VIP program could reach 200-900K yuan ($30–140K) per year. Program fees were prepaid through loans using credit card or other means. Many students have reported struggles to get refunds, even just after enrolling.
A secret audio recording of a senior manager from Wall Street English revealed that the company needed to refund students a total of 120 million yuan ($18.87 million). Many students continued to file complaints through local police stations, online courts, and consumer hotlines. Most of them now are unable to contact customer services or sales representatives.
End of Many Curriculum-Based Tutoring Businesses

A number of public education companies have announced that they would cease offering curriculum-based tutoring services to students from kindergarten through grade nine in mainland China by the end of December 2021.
Following the “Guidelines for the Classification and Identification of Off-campus Training Projects in the Compulsory Education Stage” published by the central government on November 10, 2021, this type of educational services aim to improve students’ scores in subjects like Chinese, mathematics, English, and history.
In line with the “Double Reduction Policy”, after-school education institutions are required to register as nonprofits, to adhere to the official document released by the central government of the People’s Republic of China on July 24, 2021.
| Company | Date | Announcement |
| New Oriental Education & Technology Group Inc. (EDU) | November 14, 2021 | “New Oriental Education plans to cease offering tutoring services related to academic subjects to students from kindergarten through grade nine at all learning centers across China by the end of 2021.” |
| TAL Education Group (TAL) | November 12, 2021 | “TAL Education Group plans to cease offering academic subjects tutoring to students from kindergarten through grade nine in mainland China by the end of December 2021.” |
| Gaotu Techedu Inc. (GOTU) | November 15, 2021 | “Gaotu Techedu will cease offering tutoring services related to academic subjects to students from kindergarten through grade nine by the end of 2021.” |
| Youdao, Inc. (DAO) | September 30, 2021 | “Youdao is seeking authorization from the competent local government to sell its academic business to a buyer with which Youdao is in discussions.” |
These measures impacted education from kindergarten through grade nine, which is compulsory across China and encompases 174 million students in the country, according to the “2020 National education development statistics bulletin”.
With parents desperate to give their kids the best education in spite of the uneven distribution of resources and the Gaokao system, education companies in China gained a large proportion of their revenue through curriculum-based tutoring targeted toward young learners.
| Company | Proportion of Revenue |
| New Oriental Education & Technology Group Inc. (EDU) | 50%-60% |
| TAL Education Group (TAL) | 80% |
| Youdao, Inc. (DAO) | 24% |
| GSX Techedu Inc. (GOTU) | 70% |
The shuttering of an important part of their activities has led to huge drops in these company’s stock prices: these were down 72% and 91% in the last six months.
In the wake of these regulations, some companies have announced they’re reorganizing their operations and considering expanding into other businesses:
“By leveraging its leading-edge education technology, high quality content and extensive experience, TAL will continue to operate and develop the portion of its business geared toward high school students and up, and will also explore other opportunities to provide education services in accordance with relevant rules and regulations,” announced by TAL Education Group.
One Million Jobs Affected by the “Double Reduction Policy”

As Beijing’s crackdown on Chinese education companies continues, many are shuttering a significant number of their activities, such as their curriculum-based tutoring services for young learners. As a result, tens of thousands of employees are being laid off. More than 1 million people are said to have been impacted by the policy.
We’ve compiled layoff numbers from major companies:
| Company | Number of layoffs | Number of employees before the policy |
| New Oriental Education & Technology Group Inc. (EDU) | 60000 | 100000 |
| TAL Education Group (TAL) | 90000 | 100000 |
| GSX Techedu Inc. (GOTU) | 10000 | 30000 |
| Yuanfudao | 20000 | 50000 |
| Zuoyebang | 15000 | 35000 |
| VIPKid | 6000 | 12000 |
| ByteDance Education | 5000 | 15000 |
On January 8, 2022, the founder and chairman of the New Oriental Education & Technology Group shared that:
“Due to the policy, pandemic, international relations and other reasons, the company has lost 90% of market cap and 80% of revenue in 2021. 60,000 employees were dismissed and more than 20 billion Chinese yuan ($3.14 billion) of cash expenses were generated for refund of tuition fees, layoff compensation, and rental refunds for teaching location.”
New Oriental Education & Technology Group began layoffs in mid 2021. Since then, the company has closed over 1500 learning centers across China and donated nearly 80,000 sets of desks and chairs to rural public schools. At its peak, this company had over 100,000 employees, but only around one third stayed through the end of 2021. “The remaining staff would lose half of their salary packages,” said CEO Chenggang Zhou.
On December 22 2021, the CEO of TAL Education Group reviewed the company activities since 2003 during a live streaming with its 200,000 employees in China. Zhang admitted that:
“We have relied heavily on our curriculum tutoring business and have not put much effort in well-rounded education, which will be the main trend of the Chinese education market in the future.”
On November 11, 2021, the CEO of TAL announced the company would cease offering curriculum-based tutoring services by the end the year, which has contributed to over 80% of its revenue. Before the “Double Reduction Policy”, TAL had nearly 100,000 employees. In just a few months, by the end of 2021, about 10,000 had left.
The 18-year-old company TAL that had once reached a market cap of $58 billion lost 95% of its stock value in the 6 months that followed the new regulations. The company achieved a compound revenue growth rate of 64% during the 13-year fiscal period from 2008 to 2020. From its annual financial report on February 29, 2020, it reached a revenue of $3.273 billion in the fiscal year 2020.
Suspending fundraising and withdrawing IPO applications

The Chinese online education market has experienced rapid growth since 2018 and even further at the beginning of the pandemic, when the government advocated for “Suspending Classes but Continuing Learning” via online learning platforms. In 2020 alone, over $10 billion were poured into education companies in China. Billions sere spent on marketing to acquire new students, even with deceptive strategies.
Edtech startup Yuanfudao raised $2.5 billion during its series G funding round with a valuation of over $20 billion dollars on December 24, 2020 from giant investors including Tencent, Hillhouse Capital Group, and DST Global. Similarly in December 2020, another edtech company, Zuoyebang, also completed its Series E round of $2.35 billion. Both companies had been expected to go public in the year of 2021, although they never officially commented about it.
However, in January 2021, their overexpansion via false advertising was criticised by the government. On May 10, 2021, both Zuoyebang and Yuanfudao were fined 2.5 million Chinese yuan for false advertising or deceptive marketing materials.
In May, the “Opinions on Further Alleviating the Burden of Homework and After-School Tutoring for Students in Compulsory Education” was officially reviewed and approved. After that, Yuanfudao suspended its fundraising plans, and Zuoyebang also announced the company had no clear IPO plan in May 2021. The “Double Reduction Policy” includes regulations specifically prohibiting IPO in for-profit tutoring.
Tencent-Backed Spark Education (Huohua Siwei) is an exception. Even faced with great regulation uncertainties, the company still succeeded in submitting its IPO request to the United States Securities and Exchange Commission, with a valuation of 1 billion dollars, in June 2021. The company raised a total of $593M in funding over 9 rounds. The latest funding round took place in January, 2021 during a Series E round.
Spark Education was founded in 2018 and delivers small online classes mainly for kids age 3–12. Contrary to Yuanfudao and Zuoybang, Spark Education considers itself as a “well-round education” company, focusing on mathematical and critical thinking. According to its F-1 form, the company has obtained 370K students by the end of Q1 2021 and has achieved a 501.0% increase in net revenue from 2019 to 2020.
One month before the application, 19 educational organizations were fined more than $6 million. In a meeting with investors, the CEO of Huohua Siwei still thought that they are recognized for well-rounded education and would not be affected. But it was no longer easy to raise money for education companies at that time.
On December 1, 2021, around 6 months after the application, Spark Education finally withdrew the registration. “In light of the current capital markets condition, the Company is considering other alternatives and has decided not to proceed at this time with the offering and sale of the securities proposed in the Registration Statement ”.
Tags






